Mon - Fri 7:30 am - 3:30 pm

DEDICATED TO THE
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
OF HEART DISEASE


WHO WE ARE
Pulse Cardiac Centre is a unique multidisciplinary medical clinic focused on patients with heart disease and cardiovascular risk factors. Our team includes a Cardiologist, Clinical Exercise Physiologists, a Registered Dietitian, Cardiology Technologists, and Patient Care Coordinators.

WHY WE DO IT
We are passionate about helping people achieve their optimal health. We thrive on seeing our patients regain their quality of life. And once in a while we are lucky enough to save a life.

WHAT WE DO
We treat each patient’s cardiovascular condition with the best evidence-based medical therapy. But we don’t stop there... Patients also receive written prescriptions for lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation.

COMMITTED TO EXCELLENCE
IN PATIENT CARE
COMPREHENSIVE AND
COMPASSIONATE CARE
The highest standards of professionalism

CARDIOLOGY CONSULTATION
WHAT IS A CARDIOLOGIST?
A cardiologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the heart and blood vessels. This includes conditions such as heart attacks, heart failure, heart rhythm problems, and high blood pressure. Cardiologists undergo extensive training to become experts in identifying and managing these conditions, and they use a variety of tools and techniques, such as echocardiography and cardiac catheterization, to help diagnose and treat their patients. Ultimately, their goal is to help patients maintain a healthy heart and prevent serious heart-related complications.
WHAT DO CARDIOLOGISTS AT PULSE CARDIAC CENTRE DO?
At Pulse Cardiac Centre, we focus on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention:
A cardiologist can be thought of as a detective who investigates and solves mysteries related to the heart and blood vessels. Just like a detective, a cardiologist carefully examines and analyzes all available information, including a patient's medical history, symptoms, and test results, to piece together a complete picture of what is going on with the patient's heart.
The cardiologist may order various tests, such as blood work, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and imaging tests like echocardiograms or angiograms, to gather clues and confirm their suspicions. They may also ask patients questions about their lifestyle and habits to identify risk factors for heart disease and make recommendations for lifestyle changes to prevent further problems.
Based on all of this information, the cardiologist works to make a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to the patient's specific needs. This could include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures like angioplasty or stent placement. The cardiologist will also monitor the patient's progress over time, making adjustments as necessary to ensure their heart health is optimized.
Symptoms suggestive of a heart problem include:
- Chest discomfort
- Breathing trouble
- Ankle edema (swelling)
- Palpitations
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting

AVAILABLE AT PULSE CARDIAC CENTRE
CARDIAC DIAGNOSTICS

A HOLTER MONITOR is a portable electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor that records the electrical activity of the heart continuously for between 24-hours and 14-days. Electrical impulses coordinate contractions of the heart to keep the blood flowing. The Holter monitor records these impulses to determine how fast the heart is beating, along with the rhythm, the strength, and timing of the electrical impulses.
Your healthcare provider may request a Holter monitor if you have symptoms, such as palpitations, lightheadedness, fainting, low blood pressure, ongoing fatigue (tiredness), or episodes of shortness of breath. Occasionally, we may request a Holter monitor to rule out heart rhythm abnormalities such as atrial fibrillation (AFib).
We use the newest technologies at Pulse Cardiac Centre. Gone are the days of the Holter box or going to work without showering. We use a state-of-the-art CLOUD PATCH HOLTER device that records every heartbeat for 24-hours, 5-days, 10-days, or 14-days. You can shower, exercise, and even run marathons while wearing the Cloud Patch Holter. The device uses your phone to send the data to the cloud. Often, your final report will be complete before you have even returned the device.
CARDIAC REHAB
WHO IS IT FOR?
KNOWN HEART DISEASE:
Atherosclerosis
Coronary artery disease
Angina
Heart attack
Heart failure / Cardiomyopathy
Angioplasty / Coronary Stents
Heart surgery
Arrhythmia (eg. atrial fibrillation)
Heart transplant
AT RISK OF HEART DISEASE:
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Obesity
Peripheral vascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease
Stroke·
Family history of premature heart disease
_e.jpg)
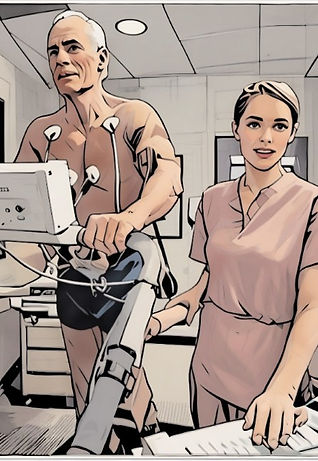
WHAT IS PULSE FIT Rx CARDIAC REHAB?
We have designed a cutting-edge cardiac rehabilitation program that is conducted in our boutique on-site gym. Our program is overseen by an experienced cardiologist and customized to meet your specific health requirements. We empower you to take charge of your cardiovascular health by creating an individualized program that includes exercise, diet, cardiovascular health education, and aggressive risk factor optimization. As your fitness improves, we modify your exercise plan to ensure maximum effectiveness. Our cardiologist follows you closely and is there with you every step of the way to optimize your medical therapy. Plus, you'll have a breathtaking view of the mountains to enhance your experience!
Designed to empower you to take charge of your cardiovascular health
Individualized program: Exercise, Diet, & Risk Factor Optimization

THE PULSE TEAM
We are committed to providing excellent clinical care through a collaborative multidisciplinary approach.

MISSION AND VALUES
1 / Best Medicine
Our mission is to prevent, treat and manage cardiovascular disease using up-to-date, evidence-based medical practice.
2 / Commitment to Patient Care
We are committed to serving our patients by delivering accessible, comprehensive and compassionate care that is of the highest quality.
3 / Ethical Care
We uphold the highest standard of ethics and moral principles.
4 / Integrity and Respect
We act with integrity and respect the well-being and dignity of each patient.
5 / Collaboration and Innovation
We value interdisciplinary collaboration and work together to innovate to improve the care we provide.
6 / Exceed Expectations
We endeavour to treat patients efficiently and effectively. We strive to exceed our patient’s expectations by improving access and the quality of our services.

PATIENT EDUCATION
CONTACT US
ADDRESS
CONTACT
HOURS
Mon - Fri
7:30 am – 3:30 pm
604-736-6442
Saturday
Closed
Sunday
Closed

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)










_edit.jpg)
